diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3512_minimum_operations_to_make_array_sum_divisible_by_k/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3512_minimum_operations_to_make_array_sum_divisible_by_k/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a1db57292
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3512_minimum_operations_to_make_array_sum_divisible_by_k/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3512_minimum_operations_to_make_array_sum_divisible_by_k
+
+// #Easy #Array #Math #2025_04_13_Time_1_ms_(100.00%)_Space_50.22_MB_(100.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minOperations(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ var sum = 0
+ for (num in nums) {
+ sum += num
+ }
+ return sum % k
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3512_minimum_operations_to_make_array_sum_divisible_by_k/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3512_minimum_operations_to_make_array_sum_divisible_by_k/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1de84f65a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3512_minimum_operations_to_make_array_sum_divisible_by_k/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+3512\. Minimum Operations to Make Array Sum Divisible by K
+
+Easy
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` and an integer `k`. You can perform the following operation any number of times:
+
+* Select an index `i` and replace `nums[i]` with `nums[i] - 1`.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of operations required to make the sum of the array divisible by `k`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,9,7], k = 5
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Perform 4 operations on `nums[1] = 9`. Now, `nums = [3, 5, 7]`.
+* The sum is 15, which is divisible by 5.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4,1,3], k = 4
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The sum is 8, which is already divisible by 4. Hence, no operations are needed.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,2], k = 6
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Perform 3 operations on `nums[0] = 3` and 2 operations on `nums[1] = 2`. Now, `nums = [0, 0]`.
+* The sum is 0, which is divisible by 6.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 1000`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 1000`
+* `1 <= k <= 100`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3513_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_i/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3513_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_i/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3be7e37b8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3513_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_i/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3513_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_i
+
+// #Medium #Array #Math #Bit_Manipulation #2025_04_13_Time_1_ms_(100.00%)_Space_89.00_MB_(100.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun uniqueXorTriplets(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = nums.size
+ return if (n < 3) n else Integer.highestOneBit(n) shl 1
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3513_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3513_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e76aab411
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3513_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+3513\. Number of Unique XOR Triplets I
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` of length `n`, where `nums` is a **permutation** of the numbers in the range `[1, n]`.
+
+A **XOR triplet** is defined as the XOR of three elements `nums[i] XOR nums[j] XOR nums[k]` where `i <= j <= k`.
+
+Return the number of **unique** XOR triplet values from all possible triplets `(i, j, k)`.
+
+A **permutation** is a rearrangement of all the elements of a set.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The possible XOR triplet values are:
+
+* `(0, 0, 0) → 1 XOR 1 XOR 1 = 1`
+* `(0, 0, 1) → 1 XOR 1 XOR 2 = 2`
+* `(0, 1, 1) → 1 XOR 2 XOR 2 = 1`
+* `(1, 1, 1) → 2 XOR 2 XOR 2 = 2`
+
+The unique XOR values are `{1, 2}`, so the output is 2.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,1,2]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The possible XOR triplet values include:
+
+* `(0, 0, 0) → 3 XOR 3 XOR 3 = 3`
+* `(0, 0, 1) → 3 XOR 3 XOR 1 = 1`
+* `(0, 0, 2) → 3 XOR 3 XOR 2 = 2`
+* `(0, 1, 2) → 3 XOR 1 XOR 2 = 0`
+
+The unique XOR values are `{0, 1, 2, 3}`, so the output is 4.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n == nums.length <= 105
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= n`
+* `nums` is a permutation of integers from `1` to `n`.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3514_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_ii/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3514_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_ii/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4ab46fd85
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3514_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_ii/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3514_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_ii
+
+// #Medium #Array #Math #Bit_Manipulation #Enumeration
+// #2025_04_13_Time_778_ms_(100.00%)_Space_61.80_MB_(100.00%)
+
+import java.util.BitSet
+
+class Solution {
+ fun uniqueXorTriplets(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val pairs: MutableSet = HashSet(mutableListOf(0))
+ var i = 0
+ val n = nums.size
+ while (i < n) {
+ for (j in i + 1..>
+
+ fun treeQueries(n: Int, edges: Array, queries: Array): IntArray {
+ adj = Array>(n + 1) { ArrayList() }
+ for (e in edges) {
+ val u = e[0]
+ val v = e[1]
+ val w = e[2]
+ adj[u].add(intArrayOf(v, w))
+ adj[v].add(intArrayOf(u, w))
+ }
+ `in` = IntArray(n + 1)
+ out = IntArray(n + 1)
+ baseDist = IntArray(n + 1)
+ parent = IntArray(n + 1)
+ depth = IntArray(n + 1)
+ edgeWeight = IntArray(n + 1)
+ dfs(1, 0, 0)
+ val fenw = Fen(n)
+ val ansList: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (query in queries) {
+ if (query[0] == 1) {
+ val u = query[1]
+ val v = query[2]
+ val newW = query[3]
+ val child: Int
+ if (parent[v] == u) {
+ child = v
+ } else if (parent[u] == v) {
+ child = u
+ } else {
+ continue
+ }
+ val diff = newW - edgeWeight[child]
+ edgeWeight[child] = newW
+ fenw.updateRange(`in`[child], out[child], diff)
+ } else {
+ val x = query[1]
+ val delta = fenw.query(`in`[x])
+ ansList.add(baseDist[x] + delta)
+ }
+ }
+ val answer = IntArray(ansList.size)
+ for (i in ansList.indices) {
+ answer[i] = ansList[i]
+ }
+ return answer
+ }
+
+ private fun dfs(node: Int, par: Int, dist: Int) {
+ parent[node] = par
+ baseDist[node] = dist
+ depth[node] = if (par == 0) 0 else depth[par] + 1
+ `in`[node] = ++timer
+ for (neighborInfo in adj[node]) {
+ val neighbor = neighborInfo[0]
+ val w = neighborInfo[1]
+ if (neighbor == par) {
+ continue
+ }
+ edgeWeight[neighbor] = w
+ dfs(neighbor, node, dist + w)
+ }
+ out[node] = timer
+ }
+
+ private class Fen(var n: Int) {
+ var fenw: IntArray = IntArray(n + 2)
+
+ fun update(i: Int, delta: Int) {
+ var i = i
+ while (i <= n) {
+ fenw[i] += delta
+ i += i and -i
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun updateRange(l: Int, r: Int, delta: Int) {
+ update(l, delta)
+ update(r + 1, -delta)
+ }
+
+ fun query(i: Int): Int {
+ var i = i
+ var sum = 0
+ while (i > 0) {
+ sum += fenw[i]
+ i -= i and -i
+ }
+ return sum
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3515_shortest_path_in_a_weighted_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3515_shortest_path_in_a_weighted_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e2bb4473f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3515_shortest_path_in_a_weighted_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+3515\. Shortest Path in a Weighted Tree
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an integer `n` and an undirected, weighted tree rooted at node 1 with `n` nodes numbered from 1 to `n`. This is represented by a 2D array `edges` of length `n - 1`, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates an undirected edge from node ui to vi with weight wi.
+
+You are also given a 2D integer array `queries` of length `q`, where each `queries[i]` is either:
+
+* `[1, u, v, w']` – **Update** the weight of the edge between nodes `u` and `v` to `w'`, where `(u, v)` is guaranteed to be an edge present in `edges`.
+* `[2, x]` – **Compute** the **shortest** path distance from the root node 1 to node `x`.
+
+Return an integer array `answer`, where `answer[i]` is the **shortest** path distance from node 1 to `x` for the ith query of `[2, x]`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
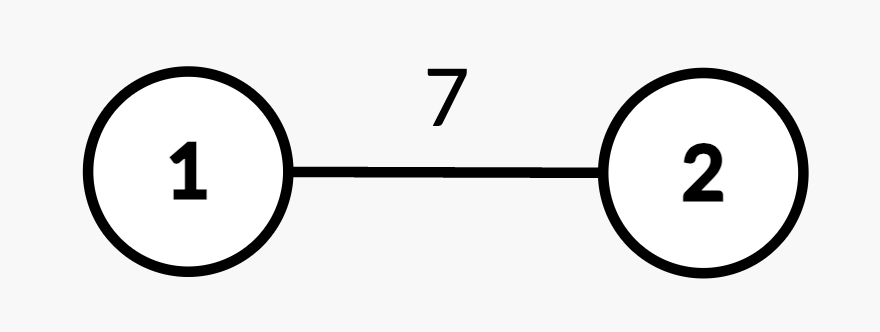
+**Input:** n = 2, edges = [[1,2,7]], queries = [[2,2],[1,1,2,4],[2,2]]
+
+**Output:** [7,4]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* Query `[2,2]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 7.
+* Query `[1,1,2,4]`: The weight of edge `(1,2)` changes from 7 to 4.
+* Query `[2,2]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
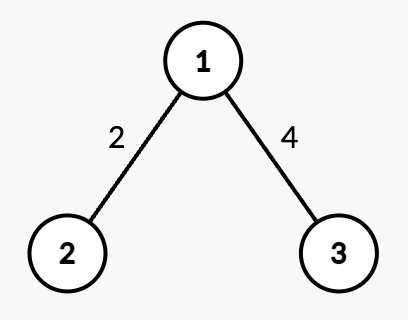
+**Input:** n = 3, edges = [[1,2,2],[1,3,4]], queries = [[2,1],[2,3],[1,1,3,7],[2,2],[2,3]]
+
+**Output:** [0,4,2,7]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* Query `[2,1]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 1 is 0.
+* Query `[2,3]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 is 4.
+* Query `[1,1,3,7]`: The weight of edge `(1,3)` changes from 4 to 7.
+* Query `[2,2]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 2.
+* Query `[2,3]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 is 7.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
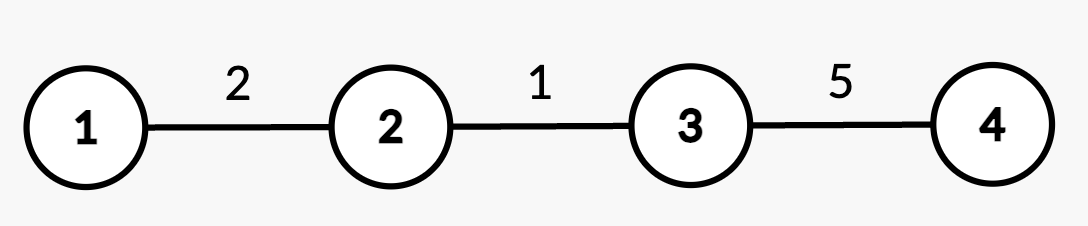
+**Input:** n = 4, edges = [[1,2,2],[2,3,1],[3,4,5]], queries = [[2,4],[2,3],[1,2,3,3],[2,2],[2,3]]
+
+**Output:** [8,3,2,5]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* Query `[2,4]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 4 consists of edges `(1,2)`, `(2,3)`, and `(3,4)` with weights `2 + 1 + 5 = 8`.
+* Query `[2,3]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 consists of edges `(1,2)` and `(2,3)` with weights `2 + 1 = 3`.
+* Query `[1,2,3,3]`: The weight of edge `(2,3)` changes from 1 to 3.
+* Query `[2,2]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 2.
+* Query `[2,3]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 consists of edges `(1,2)` and `(2,3)` with updated weights `2 + 3 = 5`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+* `edges.length == n - 1`
+* edges[i] == [ui, vi, wi]
+* 1 <= ui, vi <= n
+* 1 <= wi <= 104
+* The input is generated such that `edges` represents a valid tree.
+* 1 <= queries.length == q <= 105
+* `queries[i].length == 2` or `4`
+ * `queries[i] == [1, u, v, w']` or,
+ * `queries[i] == [2, x]`
+ * `1 <= u, v, x <= n`
+ * `(u, v)` is always an edge from `edges`.
+ * 1 <= w' <= 104
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3516_find_closest_person/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3516_find_closest_person/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5e5b925c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3516_find_closest_person/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3516_find_closest_person
+
+// #Easy #Math #2025_04_14_Time_1_ms_(100.00%)_Space_41.06_MB_(100.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.abs
+
+class Solution {
+ fun findClosest(x: Int, y: Int, z: Int): Int {
+ val d1 = abs(z - x)
+ val d2 = abs(z - y)
+ return if (d1 == d2) {
+ 0
+ } else if (d1 < d2) {
+ 1
+ } else {
+ 2
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3516_find_closest_person/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3516_find_closest_person/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..afa4e3bc2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3516_find_closest_person/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+3516\. Find Closest Person
+
+Easy
+
+You are given three integers `x`, `y`, and `z`, representing the positions of three people on a number line:
+
+* `x` is the position of Person 1.
+* `y` is the position of Person 2.
+* `z` is the position of Person 3, who does **not** move.
+
+Both Person 1 and Person 2 move toward Person 3 at the **same** speed.
+
+Determine which person reaches Person 3 **first**:
+
+* Return 1 if Person 1 arrives first.
+* Return 2 if Person 2 arrives first.
+* Return 0 if both arrive at the **same** time.
+
+Return the result accordingly.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** x = 2, y = 7, z = 4
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Person 1 is at position 2 and can reach Person 3 (at position 4) in 2 steps.
+* Person 2 is at position 7 and can reach Person 3 in 3 steps.
+
+Since Person 1 reaches Person 3 first, the output is 1.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** x = 2, y = 5, z = 6
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Person 1 is at position 2 and can reach Person 3 (at position 6) in 4 steps.
+* Person 2 is at position 5 and can reach Person 3 in 1 step.
+
+Since Person 2 reaches Person 3 first, the output is 2.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** x = 1, y = 5, z = 3
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Person 1 is at position 1 and can reach Person 3 (at position 3) in 2 steps.
+* Person 2 is at position 5 and can reach Person 3 in 2 steps.
+
+Since both Person 1 and Person 2 reach Person 3 at the same time, the output is 0.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= x, y, z <= 100`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3517_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_i/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3517_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_i/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4342095fd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3517_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_i/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3517_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_i
+
+// #Medium #String #Sorting #Counting_Sort #2025_04_14_Time_49_ms_(100.00%)_Space_52.03_MB_(100.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun smallestPalindrome(s: String): String {
+ val n = s.length
+ val m = n / 2
+ if (n == 1 || n == 2) {
+ return s
+ }
+ val fArr = s.substring(0, m).toCharArray()
+ fArr.sort()
+ var f = String(fArr)
+ val rev = StringBuilder(f).reverse()
+ if (n % 2 == 1) {
+ f += s[m]
+ }
+ return f + rev
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3517_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3517_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..14e476268
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3517_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+3517\. Smallest Palindromic Rearrangement I
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a **palindromic** string `s`.
+
+Return the **lexicographically smallest** palindromic permutation of `s`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "z"
+
+**Output:** "z"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+A string of only one character is already the lexicographically smallest palindrome.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "babab"
+
+**Output:** "abbba"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Rearranging `"babab"` → `"abbba"` gives the smallest lexicographic palindrome.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "daccad"
+
+**Output:** "acddca"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Rearranging `"daccad"` → `"acddca"` gives the smallest lexicographic palindrome.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s` consists of lowercase English letters.
+* `s` is guaranteed to be palindromic.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3518_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_ii/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3518_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_ii/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b5f8d41bc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3518_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_ii/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3518_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_ii
+
+// #Hard #String #Hash_Table #Math #Counting #Combinatorics
+// #2025_04_14_Time_27_ms_(100.00%)_Space_48.58_MB_(100.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun smallestPalindrome(inputStr: String, k: Int): String {
+ var k = k
+ val frequency = IntArray(26)
+ for (i in 0.. totalPerms) {
+ return ""
+ }
+ val firstHalfBuilder = StringBuilder()
+ for (i in 0.. 0) {
+ halfFreq[c]--
+ val perms = multinomial(halfFreq)
+ if (perms >= k) {
+ firstHalfBuilder.append(('a'.code + c).toChar())
+ break
+ } else {
+ k -= perms.toInt()
+ halfFreq[c]++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ val firstHalf = firstHalfBuilder.toString()
+ val revHalf = StringBuilder(firstHalf).reverse().toString()
+ return if (mid.code == 0) {
+ firstHalf + revHalf
+ } else {
+ firstHalf + mid + revHalf
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun multinomial(counts: IntArray): Long {
+ var tot = 0
+ for (cnt in counts) {
+ tot += cnt
+ }
+ var res: Long = 1
+ for (i in 0..25) {
+ val cnt = counts[i]
+ res = res * binom(tot, cnt)
+ if (res >= MAX_K) {
+ return MAX_K
+ }
+ tot -= cnt
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+
+ private fun binom(n: Int, k: Int): Long {
+ var k = k
+ if (k > n) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (k > n - k) {
+ k = n - k
+ }
+ var result: Long = 1
+ for (i in 1..k) {
+ result = result * (n - i + 1) / i
+ if (result >= MAX_K) {
+ return MAX_K
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private const val MAX_K: Long = 1000001
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3518_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3518_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a16bf1d62
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3518_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+3518\. Smallest Palindromic Rearrangement II
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a **palindromic** string `s` and an integer `k`.
+
+Return the **k-th** **lexicographically smallest** palindromic permutation of `s`. If there are fewer than `k` distinct palindromic permutations, return an empty string.
+
+**Note:** Different rearrangements that yield the same palindromic string are considered identical and are counted once.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abba", k = 2
+
+**Output:** "baab"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The two distinct palindromic rearrangements of `"abba"` are `"abba"` and `"baab"`.
+* Lexicographically, `"abba"` comes before `"baab"`. Since `k = 2`, the output is `"baab"`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aa", k = 2
+
+**Output:** ""
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* There is only one palindromic rearrangement: `"aa"`.
+* The output is an empty string since `k = 2` exceeds the number of possible rearrangements.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "bacab", k = 1
+
+**Output:** "abcba"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The two distinct palindromic rearrangements of `"bacab"` are `"abcba"` and `"bacab"`.
+* Lexicographically, `"abcba"` comes before `"bacab"`. Since `k = 1`, the output is `"abcba"`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 104
+* `s` consists of lowercase English letters.
+* `s` is guaranteed to be palindromic.
+* 1 <= k <= 106
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3519_count_numbers_with_non_decreasing_digits/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3519_count_numbers_with_non_decreasing_digits/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..566c76ef4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3519_count_numbers_with_non_decreasing_digits/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3519_count_numbers_with_non_decreasing_digits
+
+// #Hard #String #Dynamic_Programming #Math
+// #2025_04_14_Time_31_ms_(100.00%)_Space_46.39_MB_(100.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun countNumbers(l: String, r: String, b: Int): Int {
+ val ans1 = find(r.toCharArray(), b)
+ val start = subTractOne(l.toCharArray())
+ val ans2 = find(start, b)
+ return ((ans1 - ans2) % 1000000007L).toInt()
+ }
+
+ private fun find(arr: CharArray, b: Int): Long {
+ val nums = convertNumToBase(arr, b)
+ val dp = Array>>(nums.size) { Array>(2) { arrayOfNulls(11) } }
+ return solve(0, nums, 1, b, 0, dp) - 1
+ }
+
+ private fun solve(i: Int, arr: IntArray, tight: Int, base: Int, last: Int, dp: Array>>): Long {
+ if (i == arr.size) {
+ return 1L
+ }
+ if (dp[i][tight][last] != null) {
+ return dp[i][tight][last]!!
+ }
+ var till = base - 1
+ if (tight == 1) {
+ till = arr[i]
+ }
+ var ans: Long = 0
+ for (j in 0..till) {
+ if (j >= last) {
+ ans = (ans + solve(i + 1, arr, tight and (if (j == arr[i]) 1 else 0), base, j, dp))
+ }
+ }
+ dp[i][tight][last] = ans
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun subTractOne(arr: CharArray): CharArray {
+ val n = arr.size
+ var i = n - 1
+ while (i >= 0 && arr[i] == '0') {
+ arr[i--] = '9'
+ }
+ val x = arr[i].code - '0'.code - 1
+ arr[i] = (x + '0'.code).toChar()
+ var j = 0
+ var idx = 0
+ while (j < n && arr[j] == '0') {
+ j++
+ }
+ val res = CharArray(n - j)
+ for (k in j.. = ArrayList()
+ var len = n
+ while (len > 0) {
+ var rem = 0
+ val next = IntArray(len)
+ var newLen = 0
+ var j = 0
+ while (j < len) {
+ val cur = rem * 10L + num[j]
+ val q = (cur / base).toInt()
+ rem = (cur % base).toInt()
+ if (newLen > 0 || q != 0) {
+ next[newLen] = q
+ newLen++
+ }
+ j++
+ }
+ temp.add(rem)
+ num = next
+ len = newLen
+ }
+ val res = IntArray(temp.size)
+ var k = 0
+ val size = temp.size
+ while (k < size) {
+ res[k] = temp[size - 1 - k]!!
+ k++
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3519_count_numbers_with_non_decreasing_digits/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3519_count_numbers_with_non_decreasing_digits/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f3809376f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3519_count_numbers_with_non_decreasing_digits/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+3519\. Count Numbers with Non-Decreasing Digits
+
+Hard
+
+You are given two integers, `l` and `r`, represented as strings, and an integer `b`. Return the count of integers in the inclusive range `[l, r]` whose digits are in **non-decreasing** order when represented in base `b`.
+
+An integer is considered to have **non-decreasing** digits if, when read from left to right (from the most significant digit to the least significant digit), each digit is greater than or equal to the previous one.
+
+Since the answer may be too large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** l = "23", r = "28", b = 8
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The numbers from 23 to 28 in base 8 are: 27, 30, 31, 32, 33, and 34.
+* Out of these, 27, 33, and 34 have non-decreasing digits. Hence, the output is 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** l = "2", r = "7", b = 2
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The numbers from 2 to 7 in base 2 are: 10, 11, 100, 101, 110, and 111.
+* Out of these, 11 and 111 have non-decreasing digits. Hence, the output is 2.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= l.length <= r.length <= 100`
+* `2 <= b <= 10`
+* `l` and `r` consist only of digits.
+* The value represented by `l` is less than or equal to the value represented by `r`.
+* `l` and `r` do not contain leading zeros.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3512_minimum_operations_to_make_array_sum_divisible_by_k/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3512_minimum_operations_to_make_array_sum_divisible_by_k/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c76740d2f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3512_minimum_operations_to_make_array_sum_divisible_by_k/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3512_minimum_operations_to_make_array_sum_divisible_by_k
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minOperations(intArrayOf(3, 9, 7), 5), equalTo(4))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minOperations(intArrayOf(4, 1, 3), 4), equalTo(0))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations3() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minOperations(intArrayOf(3, 2), 6), equalTo(5))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3513_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_i/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3513_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_i/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..56a2fcddb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3513_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_i/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3513_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_i
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun uniqueXorTriplets() {
+ assertThat(Solution().uniqueXorTriplets(intArrayOf(1, 2)), equalTo(2))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun uniqueXorTriplets2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().uniqueXorTriplets(intArrayOf(3, 1, 2)), equalTo(4))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3514_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_ii/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3514_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_ii/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4ba4e888e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3514_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_ii/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3514_number_of_unique_xor_triplets_ii
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun uniqueXorTriplets() {
+ assertThat(Solution().uniqueXorTriplets(intArrayOf(1, 3)), equalTo(2))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun uniqueXorTriplets2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().uniqueXorTriplets(intArrayOf(6, 7, 8, 9)),
+ equalTo(4),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3515_shortest_path_in_a_weighted_tree/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3515_shortest_path_in_a_weighted_tree/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..9d3016f87
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3515_shortest_path_in_a_weighted_tree/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3515_shortest_path_in_a_weighted_tree
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun treeQueries() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .treeQueries(
+ 2,
+ arrayOf(intArrayOf(1, 2, 7)),
+ arrayOf(intArrayOf(2, 2), intArrayOf(1, 1, 2, 4), intArrayOf(2, 2)),
+ ),
+ equalTo(intArrayOf(7, 4)),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun treeQueries2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .treeQueries(
+ 3,
+ arrayOf(intArrayOf(1, 2, 2), intArrayOf(1, 3, 4)),
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(2, 1),
+ intArrayOf(2, 3),
+ intArrayOf(1, 1, 3, 7),
+ intArrayOf(2, 2),
+ intArrayOf(2, 3),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(intArrayOf(0, 4, 2, 7)),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun treeQueries3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .treeQueries(
+ 4,
+ arrayOf(intArrayOf(1, 2, 2), intArrayOf(2, 3, 1), intArrayOf(3, 4, 5)),
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(2, 4),
+ intArrayOf(2, 3),
+ intArrayOf(1, 2, 3, 3),
+ intArrayOf(2, 2),
+ intArrayOf(2, 3),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(intArrayOf(8, 3, 2, 5)),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3516_find_closest_person/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3516_find_closest_person/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..492827150
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3516_find_closest_person/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3516_find_closest_person
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun findClosest() {
+ assertThat(Solution().findClosest(2, 7, 4), equalTo(1))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun findClosest2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().findClosest(2, 5, 6), equalTo(2))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun findClosest3() {
+ assertThat(Solution().findClosest(1, 5, 3), equalTo(0))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3517_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_i/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3517_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_i/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a05249473
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3517_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_i/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3517_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_i
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun smallestPalindrome() {
+ assertThat(Solution().smallestPalindrome("z"), equalTo("z"))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun smallestPalindrome2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().smallestPalindrome("babab"),
+ equalTo("abbba"),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun smallestPalindrome3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().smallestPalindrome("daccad"),
+ equalTo("acddca"),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3518_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_ii/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3518_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_ii/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b1f5d4744
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3518_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_ii/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3518_smallest_palindromic_rearrangement_ii
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun smallestPalindrome() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().smallestPalindrome("abba", 2),
+ equalTo("baab"),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun smallestPalindrome2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().smallestPalindrome("aa", 2), equalTo(""))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun smallestPalindrome3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().smallestPalindrome("bacab", 1),
+ equalTo("abcba"),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3519_count_numbers_with_non_decreasing_digits/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3519_count_numbers_with_non_decreasing_digits/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..dec21d7c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3519_count_numbers_with_non_decreasing_digits/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3519_count_numbers_with_non_decreasing_digits
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun countNumbers() {
+ assertThat(Solution().countNumbers("23", "28", 8), equalTo(3))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun countNumbers2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().countNumbers("2", "7", 2), equalTo(2))
+ }
+}