This program uses journalctl and systemctl to watch for changes in your services, and top for metrics about those services, and delivers current status to MQTT. It will also publish Home Assistant MQTT Discovery messages so that (binary) sensors automatically show up in Home Assistant.
The focus lies on long-running services with continuous uptime, instead of single or one-shot services, as the stats being reported as well as the child PIDs being refreshed every stats_record_seconds. For services with a lifespan comparable to this interval, the reported stats will not be accurate. Further, as the library uses top and matches the services with their respective PIDs, including child PIDs from subprocesses, it is also not suited for monitoring services which spawn regularly new threads.
This is part of a family of similar tools:
It is available as python package on pypi/systemctl2mqtt.
pip install systemctl2mqtt
systemctl2mqtt --name MySystemName --events -vvvvvUsage
from systemctl2mqtt import systemctl2Mqtt, DEFAULT_CONFIG
cfg = Systemctl2MqttConfig({
**DEFAULT_CONFIG,
"host": "mosquitto",
"enable_events": True
})
try:
systemctl2mqtt = Systemctl2Mqtt(cfg)
systemctl2mqtt.loop_busy()
except Exception as ex:
# Do somethingYou can use environment variables to control the behavior.
| Config | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
log_level |
INFO |
Set to DEBUG,INFO,WARN,ERROR,CRITICAL to enable different levels of verbosity. |
systemctl2mqtt_hostname |
systemctl2mqtt Hostname | The hostname of your host, if you want to overwrite it. |
homeassistant_prefix |
homeassistant |
The prefix for Home Assistant discovery. Must be the same as discovery_prefix in your Home Assistant configuration. |
mqtt_client_id |
mqtt2discord |
The client id to send to the MQTT broker. |
mqtt_host |
localhost |
The MQTT broker to connect to. |
mqtt_port |
1883 |
The port on the broker to connect to. |
mqtt_user |
The user to send to the MQTT broker. Leave unset to disable authentication. | |
mqtt_password |
The password to send to the MQTT broker. Leave unset to disable authentication. | |
mqtt_timeout |
30 |
The timeout for the MQTT connection. |
mqtt_topic_prefix |
systemctl |
The MQTT topic prefix. With the default data will be published to systemctl/<hostname>. |
mqtt_qos |
1 |
The MQTT QOS level |
service_whitelist |
Define a whitelist for services to consider, if empty, everything is monitored. The entries are either match as literal strings or as regex. | |
service_blacklist |
Define a blacklist for services to consider, takes priority over whitelist. The entries are either match as literal strings or as regex. | |
destroyed_service_ttl |
86400 |
How long, in seconds, before destroyed services are removed from Home Assistant. Services won't be removed if the service is restarted before the TTL expires. |
stats_record_seconds |
30 |
The number of seconds to record state and make an average |
enable_events |
0 |
1 Or 0 for processing events |
enable_stats |
0 |
1 Or 0 for processing statistics |
Data is published to the topic systemctl/<hostname>/events using JSON serialization. It will arrive whenever a change happens and its type can be inspected in type_definitions.py or the documentation.
Data is also published to the topic systemctl/<hostname>/stats using JSON serialization. It will arrive every STATS_RECORD_SECONDS seconds or so can be inspected in type_definitions.py or the documentation.
Once systemctl2mqtt is collecting data and publishing it to MQTT, it's rather trivial to use the data in Home Assistant.
A few assumptions:
- Home Assistant is already configured to use a MQTT broker. Setting up MQTT and HA is beyond the scope of this documentation. However, there are a lot of great tutorials on YouTube. An external broker (or as add-on) like Mosquitto will need to be installed and the HA MQTT integration configured.
- The HA MQTT integration is configured to use
homeassistantas the MQTT autodiscovery prefix. This is the default for the integration and also the default forsystemctl2mqtt. If you have changed this from the default, use the--prefixparameter to specify the correct one. - You're not using TLS to connect to the MQTT broker. Currently
systemctl2mqttonly works with unencrypted connections. Username / password authentication can be specified with the--usernameand--passwordparameters, but TLS encryption is not yet supported.
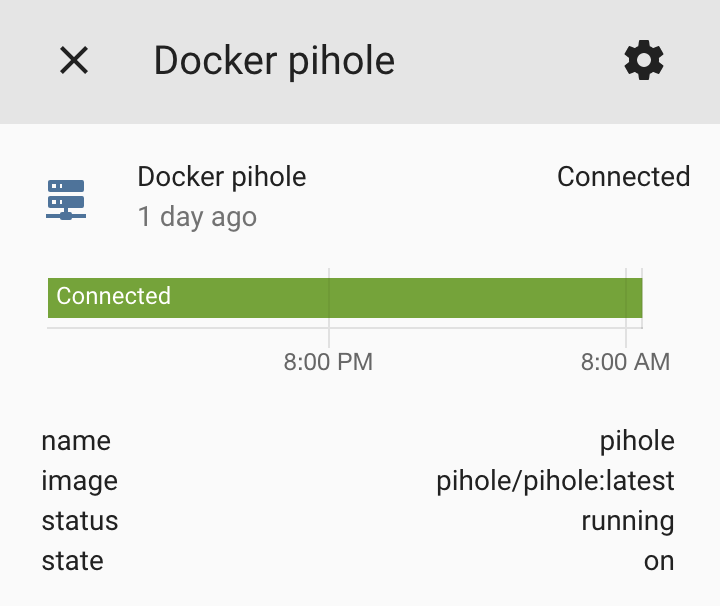
After you start the service (binary) sensors should show up in Home Assistant immediately. Look for sensors that start with (binary_)sensor.systemctl. Metadata about the container will be available as attributes for events, which you can then expose using template sensors if you wish.
Using mkdocs, the documentation and reference is generated and available on github pages.
Setup the dev environment using VSCode, it is highly recommended.
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements_dev.txtInstall pre-commit
pre-commit install
# Run the commit hooks manually
pre-commit run --all-filesFollowing VSCode integrations may be helpful:
It is only possible to release a final version on the master branch. For it to pass the gates of the publish workflow, it must have the same version in the tag, the setup.cfg, the bring_api/__init__.py and an entry in the CHANGELOG.md file.
To release a prerelease version, no changelog entry is required, but it can only happen on a feature branch (not master branch). Also, prerelease versions are marked as such in the github release page.
This is inspired from my other repo docker2mqtt.