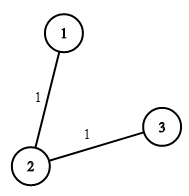
There are n houses in a village. We want to supply water for all the houses by building wells and laying pipes.
For each house i, we can either build a well inside it directly with cost wells[i - 1] (note the -1 due to 0-indexing), or pipe in water from another well to it. The costs to lay pipes between houses are given by the array pipes where each pipes[j] = [house1j, house2j, costj] represents the cost to connect house1j and house2j together using a pipe. Connections are bidirectional, and there could be multiple valid connections between the same two houses with different costs.
Return the minimum total cost to supply water to all houses.
Example 1:
Input: n = 3, wells = [1,2,2], pipes = [[1,2,1],[2,3,1]] Output: 3 Explanation: The image shows the costs of connecting houses using pipes. The best strategy is to build a well in the first house with cost 1 and connect the other houses to it with cost 2 so the total cost is 3.
Example 2:
Input: n = 2, wells = [1,1], pipes = [[1,2,1],[1,2,2]] Output: 2 Explanation: We can supply water with cost two using one of the three options: Option 1: - Build a well inside house 1 with cost 1. - Build a well inside house 2 with cost 1. The total cost will be 2. Option 2: - Build a well inside house 1 with cost 1. - Connect house 2 with house 1 with cost 1. The total cost will be 2. Option 3: - Build a well inside house 2 with cost 1. - Connect house 1 with house 2 with cost 1. The total cost will be 2. Note that we can connect houses 1 and 2 with cost 1 or with cost 2 but we will always choose the cheapest option.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 104wells.length == n0 <= wells[i] <= 1051 <= pipes.length <= 104pipes[j].length == 31 <= house1j, house2j <= n0 <= costj <= 105house1j != house2j
Union find.
class Solution:
def minCostToSupplyWater(
self, n: int, wells: List[int], pipes: List[List[int]]
) -> int:
def find(x: int) -> int:
if p[x] != x:
p[x] = find(p[x])
return p[x]
for i, w in enumerate(wells, 1):
pipes.append([0, i, w])
pipes.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
p = list(range(n + 1))
ans = 0
for i, j, c in pipes:
pa, pb = find(i), find(j)
if pa == pb:
continue
p[pa] = pb
ans += c
n -= 1
if n == 0:
break
return ansclass Solution {
private int[] p;
public int minCostToSupplyWater(int n, int[] wells, int[][] pipes) {
var nums = new int[n + pipes.length][0];
int j = 0;
for (var pipe : pipes) {
nums[j++] = pipe;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
nums[j++] = new int[] {0, i + 1, wells[i]};
}
Arrays.sort(nums, (a, b) -> a[2] - b[2]);
p = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
}
int ans = 0;
for (var x : nums) {
int pa = find(x[0]), pb = find(x[1]);
if (pa == pb) {
continue;
}
ans += x[2];
p[pa] = pb;
if (--n == 0) {
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
private int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
}class Solution {
public:
int minCostToSupplyWater(int n, vector<int>& wells, vector<vector<int>>& pipes) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
pipes.push_back({0, i + 1, wells[i]});
}
sort(pipes.begin(), pipes.end(), [](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) {
return a[2] < b[2];
});
int p[n + 1];
iota(p, p + n + 1, 0);
function<int(int)> find = [&](int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
};
int ans = 0;
for (const auto& x : pipes) {
int pa = find(x[0]), pb = find(x[1]);
if (pa == pb) {
continue;
}
p[pa] = pb;
ans += x[2];
if (--n == 0) {
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
};func minCostToSupplyWater(n int, wells []int, pipes [][]int) (ans int) {
for i, w := range wells {
pipes = append(pipes, []int{0, i + 1, w})
}
sort.Slice(pipes, func(i, j int) bool { return pipes[i][2] < pipes[j][2] })
p := make([]int, n+1)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
}
var find func(int) int
find = func(x int) int {
if p[x] != x {
p[x] = find(p[x])
}
return p[x]
}
for _, x := range pipes {
pa, pb := find(x[0]), find(x[1])
if pa == pb {
continue
}
p[pa] = pb
ans += x[2]
n--
if n == 0 {
break
}
}
return
}function minCostToSupplyWater(n: number, wells: number[], pipes: number[][]): number {
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
pipes.push([0, i + 1, wells[i]]);
}
pipes.sort((a, b) => a[2] - b[2]);
const p = new Array(n + 1).fill(0).map((_, i) => i);
const find = (x: number): number => {
if (p[x] !== x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
};
let ans = 0;
for (const [i, j, c] of pipes) {
const pa = find(i);
const pb = find(j);
if (pa === pb) {
continue;
}
p[pa] = pb;
ans += c;
if (--n === 0) {
break;
}
}
return ans;
}