forked from jainaman224/Algo_Ds_Notes
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Create Readme.md (jainaman224#2480) (jainaman224#2888)
- Loading branch information
1 parent
7d474f3
commit e7cfc50
Showing
1 changed file
with
137 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,137 @@ | ||
| # Boyer Moore Algorithm | ||
| The Boyer Moore Algorithm was established by Robert Boyer and J Strother Moore in 1977. The Boyer Moore (B-M) String search algorithm is a particularly efficient algorithm and has served as a standard benchmark for string search algorithm ever since.The algorithm takes a 'backward' approach: the pattern string (P) is aligned with the start of the text string (T), and then compares the characters of a pattern from right to left, beginning with rightmost character.If a character is compared that is not within the pattern, no match can be found by analyzing any further aspects at this position so the pattern can be changed entirely past the mismatching character. | ||
| ## **Explanation** | ||
| The B-M algorithm ,for deciding the possible shifts, uses two preprocessing strategies simultaneously. Whenever a mismatch occurs, the algorithm calculates a variation using both approaches and selects the more significant shift thus, if make use of the most effective strategy for each case. | ||
| The two strategies are called heuristics of B - M as they are used to reduce the search. They are: | ||
| 1) Bad Character Heuristics | ||
| 2) Good Suffix Heuristics | ||
|
|
||
| ***Bad Character Heuristic*** | ||
| The idea of bad character heuristic is simple. The character of the text which doesn’t match with the current character of the pattern is called the Bad Character. Upon mismatch, we shift the pattern until – | ||
| 1) The mismatch becomes a match | ||
| 2) Pattern P move past the mismatched character. | ||
| + Case 1 – Mismatch become match | ||
| We will lookup the position of last occurrence of mismatching character in pattern and if mismatching character exist in pattern then we’ll shift the pattern such that it get aligned to the mismatching character in text T. | ||
| 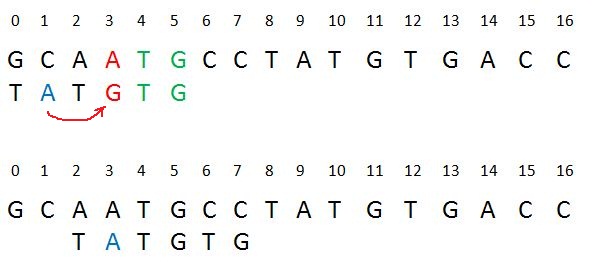 | ||
| + Case 2 – Pattern move past the mismatch character | ||
| We’ll lookup the position of last occurrence of mismatching character in pattern and if character does not exist we will shift pattern past the mismatching character. | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ***Good Suffix Heuristic*** | ||
| Let t be substring of text T which is matched with substring of pattern P. Now we shift pattern until : | ||
| 1) Another occurrence of t in P matched with t in T. | ||
| 2) A prefix of P, which matches with suffix of t | ||
| 3) P moves past t | ||
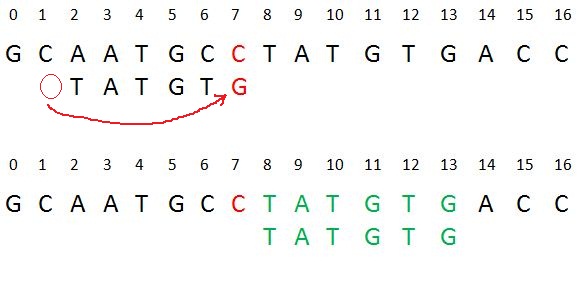
| + Case 1: Another occurrence of t in P matched with t in T | ||
| Pattern P might contain few more occurrences of t. In such case, we will try to shift the pattern to align that occurrence with t in text T. For example- | ||
|  | ||
| + Case 2: A prefix of P, which matches with suffix of t in T | ||
| It is not always likely that we will find the occurrence of t in P. Sometimes there is no occurrence at all, in such cases sometimes we can search for some suffix of t matching with some prefix of P and try to align them by shifting P. For example – | ||
|  | ||
| + Case 3: P moves past t | ||
| If the above two cases are not satisfied, we will shift the pattern past the t. For example – | ||
|  | ||
| ## Algorithm | ||
| ``` | ||
| fullSuffixMatch(shiftArray, borderArray, pattern) | ||
| Input: Array to store shift locations, the border array and the pattern to search | ||
| Output: Fill the shift array and the border array | ||
| Begin | ||
| n := pattern length | ||
| j := n | ||
| j := n + 1 | ||
| borderArray[i] := j | ||
| while i > 0, do | ||
| while j <= n AND pattern[i - 1] ≠ pattern[j - 1], do | ||
| if shiftArray[j] = 0, then | ||
| shiftArray[j] := j - i; | ||
| j := borderArray[j]; | ||
| done | ||
| decrease i and j by 1 | ||
| borderArray[i] := j | ||
| done | ||
| End | ||
| partialSuffixMatch(shiftArray, borderArray, pattern) | ||
| Input: Array to store shift locations, the border array and the pattern to search | ||
| Output: Fill the shift array and the border array | ||
| Begin | ||
| n := pattern length | ||
| j := borderArray[0] | ||
| for index of all characters ‘i’ of pattern, do | ||
| if shiftArray[i] = 0, then | ||
| shiftArray[i] := j | ||
| if i = j then | ||
| j := borderArray[j] | ||
| done | ||
| End | ||
| searchPattern(text, pattern) | ||
| Input: The main text and the pattern, that will be searched | ||
| Output: The indexes where the pattern is found | ||
| Begin | ||
| patLen := pattern length | ||
| strLen := text size | ||
| for all entries of shiftArray, do | ||
| set all entries to 0 | ||
| done | ||
| call fullSuffixMatch(shiftArray, borderArray, pattern) | ||
| call partialSuffixMatch(shiftArray, borderArray, pattern) | ||
| shift := 0 | ||
| while shift <= (strLen - patLen), do | ||
| j := patLen -1 | ||
| while j >= 0 and pattern[j] = text[shift + j], do | ||
| decrease j by 1 | ||
| done | ||
| if j < 0, then | ||
| print the shift as, there is a match | ||
| shift := shift + shiftArray[0] | ||
| else | ||
| shift := shift + shiftArray[j + 1] | ||
| done | ||
| End | ||
| ``` | ||
| ## Examples | ||
| Input: txt[] = "THIS IS A TEST TEXT" | ||
| pat[] = "TEST" | ||
| Output: Pattern found at index 10 | ||
| Input: txt[] = "AABAACAADAABAABA" | ||
| pat[] = "AABA" | ||
| Output: Pattern found at index 0 | ||
| Pattern found at index 9 | ||
| Pattern found at index 12 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
| ## Time Complexity | ||
| Preprocessing Time Complexity: O(|∑|) | ||
| Matching Time Complexity: (O ((n - m + 1) + |∑|)) | ||
| ## Implementation | ||
| - [C Code](https://github.com/jainaman224/Algo_Ds_Notes/blob/da4a40a70f/Boyer_Moore_Algorithm/Boyer_Moore.c) | ||
| - [C++ Code](https://github.com/jainaman224/Algo_Ds_Notes/blob/da4a40a70f/Boyer_Moore_Algorithm/Boyer_Moore.cpp ) | ||
| - [C# Code](https://github.com/jainaman224/Algo_Ds_Notes/blob/da4a40a70f/Boyer_Moore_Algorithm/Boyer_Moore.cs) | ||
| - [Go Code](https://github.com/jainaman224/Algo_Ds_Notes/blob/da4a40a70f/Boyer_Moore_Algorithm/Boyer_Moore.go) | ||
| - [Java Code](https://github.com/jainaman224/Algo_Ds_Notes/blob/da4a40a70f/Boyer_Moore_Algorithm/Boyer_Moore.java) | ||
| - [Kotlin Code](https://github.com/jainaman224/Algo_Ds_Notes/blob/da4a40a70f/Boyer_Moore_Algorithm/Boyer_Moore.kt) | ||
| - [Python Code](https://github.com/jainaman224/Algo_Ds_Notes/blob/da4a40a70f/Boyer_Moore_Algorithm/Boyer_Moore.py) | ||
| ## References | ||
| + Image source: [https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/boyer-moore-algorithm-for-pattern-searching/](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/boyer-moore-algorithm-for-pattern-searching/) | ||
| #### Websites: | ||
| 1. [https://www.javatpoint.com/daa-boyer-moore-algorithm](https://www.javatpoint.com/daa-boyer-moore-algorithm) | ||
| 2. [https://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/courses/compsci369s1c/lectures/GG-notes/CS369-StringAlgs.pdf](https://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/courses/compsci369s1c/lectures/GG-notes/CS369-StringAlgs.pdf) | ||
| 3. [geeksforgeeks.org/boyer-moore-algorithm-good-suffix-heuristic/?ref=rp](geeksforgeeks.org/boyer-moore-algorithm-good-suffix-heuristic/?ref=rp) |