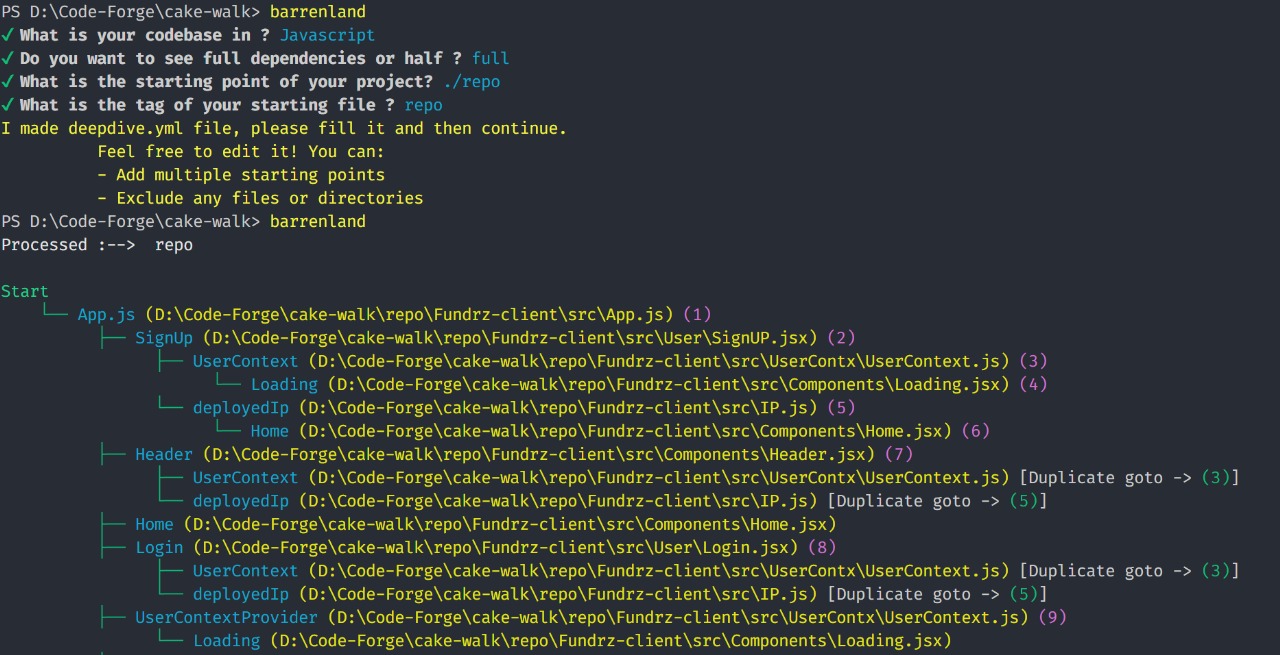
Barrenland is a tool that simplifies codebase exploration by visualizing import dependencies as a hierarchical structure. This helps developers understand the relationships between files, improve code maintainability, and facilitate better team collaboration. By making the import hierarchy visually clear, Barrenland ensures that navigating through large projects is less overwhelming and more efficient.
When working on a new project, encountering numerous imports and their interdependencies can often be a challenge. Barrenland provides a way to visualize this hierarchy, making it easier to understand how files are connected through imports. This insight can significantly enhance productivity and reduce the time spent trying to track down issues or understand the flow of data.
Github - https://github.com/SharkFishDeveloper/Cake-walk
- Visualize Import Hierarchies: Easily understand how files are interconnected through imports.
- Simplify Codebase Exploration: Navigate complex codebases more efficiently by visualizing the import structure in a hierarchical format.
- Identify Potential Issues: Pinpoint the root cause of bugs by analyzing import dependencies. By examining the import hierarchy, it's easier to track if a bug originates from downstream dependencies (imports below) rather than upstream ones (files that are imported).
- Support for JavaScript and TypeScript: Works seamlessly with popular frameworks like Node.js, React, and Next.js.
- Exclusion of Unnecessary Folders: Specify folders (like
node_modulesordist) that can be excluded from the analysis, so that only relevant files and imports are considered.
Currently, Barrenland supports JavaScript and TypeScript, including major frameworks and environments such as:
- Node.js
- React
- Next.js
Support for additional programming languages and frameworks will be added in the future.
Global Installation:
To install Barrenland globally, run the following command:
npm i -g barrenlandOnce installed globally, you can run the tool by typing:
barrenland
This command will initiate the tool and create a barrenland.yml file if it doesn't already exist. The .yml file is used to specify the starting point, tags, and excluded folders for the analysis.
Again type barreland so start the tool.
Local Installation:
If you prefer to install Barrenland locally to your project, you can use the following command:
npm i barrenland
After installation, you can run Barrenland using:
npx barrenland
Configuration: barrenland.yml The barrenland.yml file will be generated in your project’s root directory after the first run, unless it already exists. This configuration file allows you to customize the behavior of Barrenland, including which files and folders to analyze, and which to exclude.
Again type barreland so start the tool.
Fields in barrenland.yml: start: The entry point(s) from which the analysis will begin. This can be a single file or a folder containing multiple files. tag: A unique name for start file. excludeFolders: An optional array where you can specify folders that should be excluded from the dependency analysis (e.g., node_modules, dist, etc.).
start:
- path: ./src/index.js
tag: index.js
- path: ./src/component
tag: component.js
excludeFolders:
- ./src/test
- ./node_modules
In this example, the analysis will begin at ./src/index.js and ./src/components, and it will exclude ./src/test and ./node_modules from the hierarchy.