eta is a command line tool that takes two arguments:
- A target value
- A command to inspect the current progress value
eta will execute the given command once every second, look for the first number in the commands output, and estimate the time until it reaches the given target value.
When using --cont, command runs continuously, and eta will read the output line by line to determine progress.
See man page for full documentation.
sudo apt install eta
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:aioobe/ppa
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install eta
Download repo, build and install manually:
make
make install
Use du -bs to monitor the size of a directory.
To avoid running an ssh command every second, you can lower the rate with --interval or use --cont and a single ssh invocation with a while loop. (Examples 3 and 4 illustrate the use of --cont.)
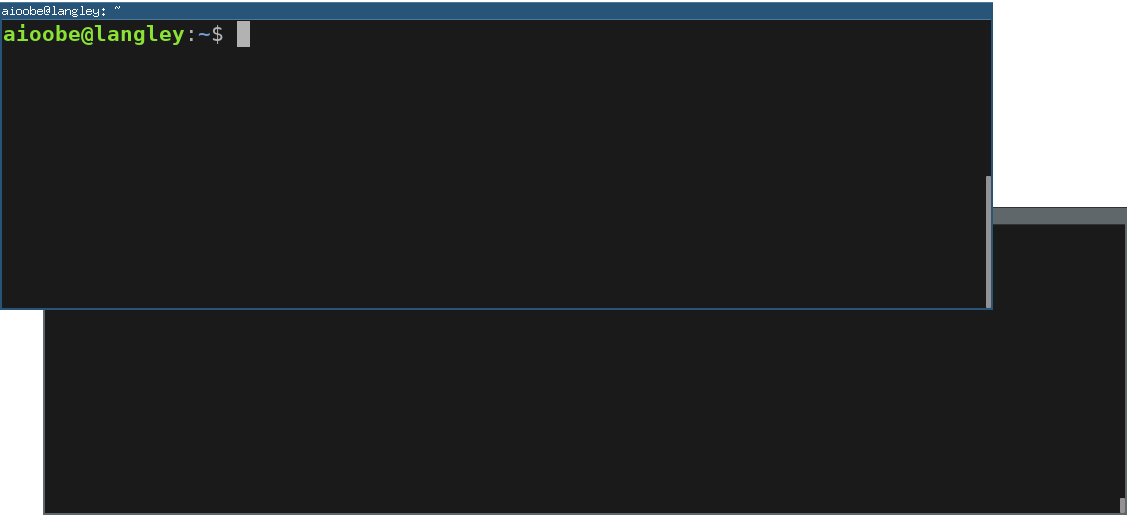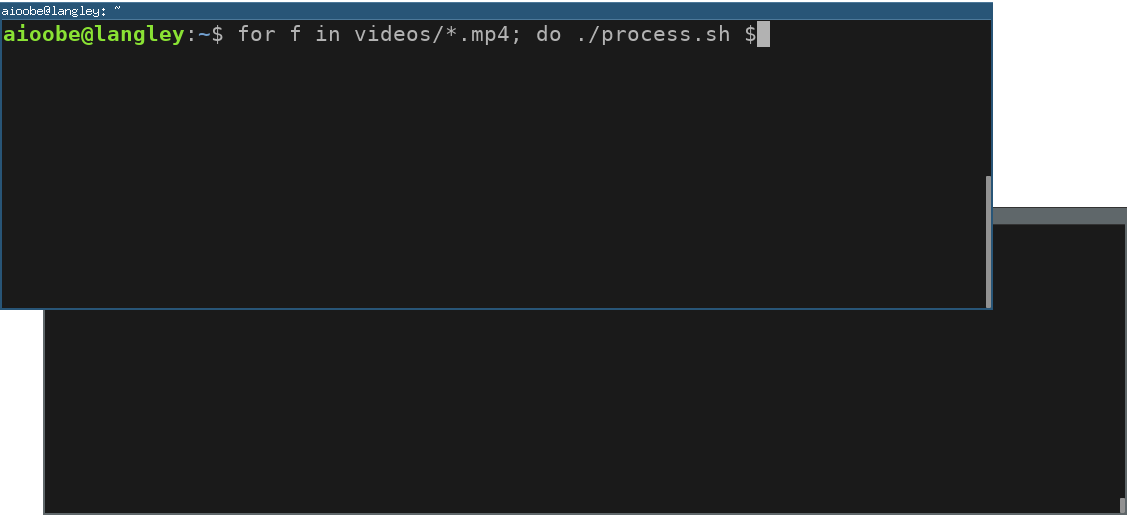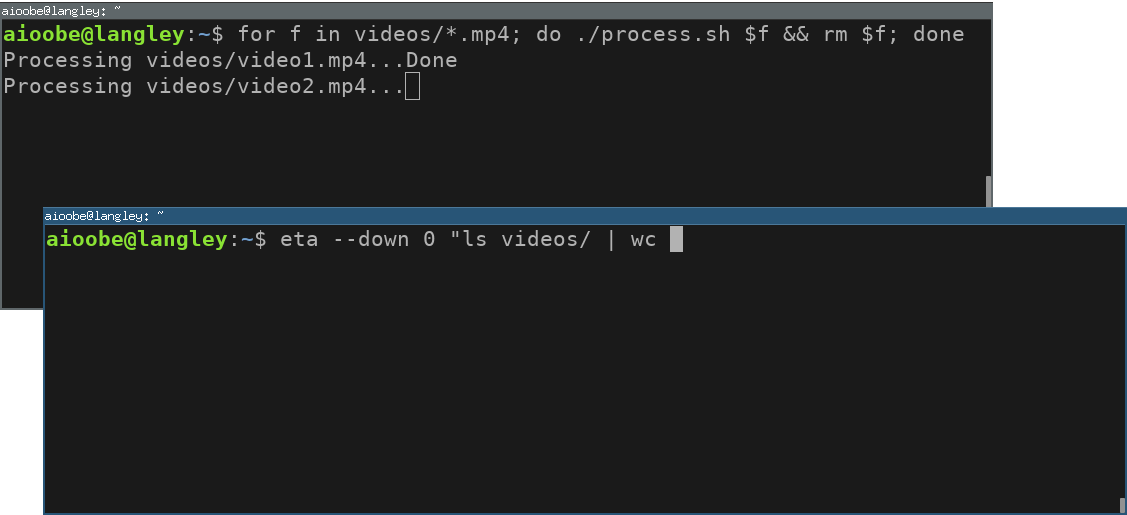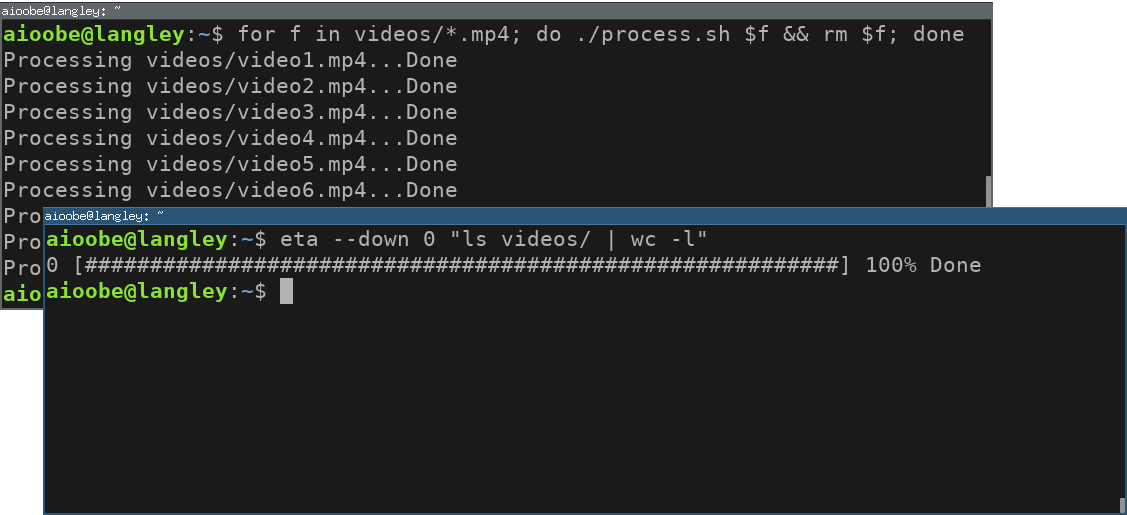
Use ls | wc -l to monitor the number of files in a directory.
If the resized directory is initially non empty, you can use --start initial which tells eta to use the first value read (instead of 0) as the 0% progress value.
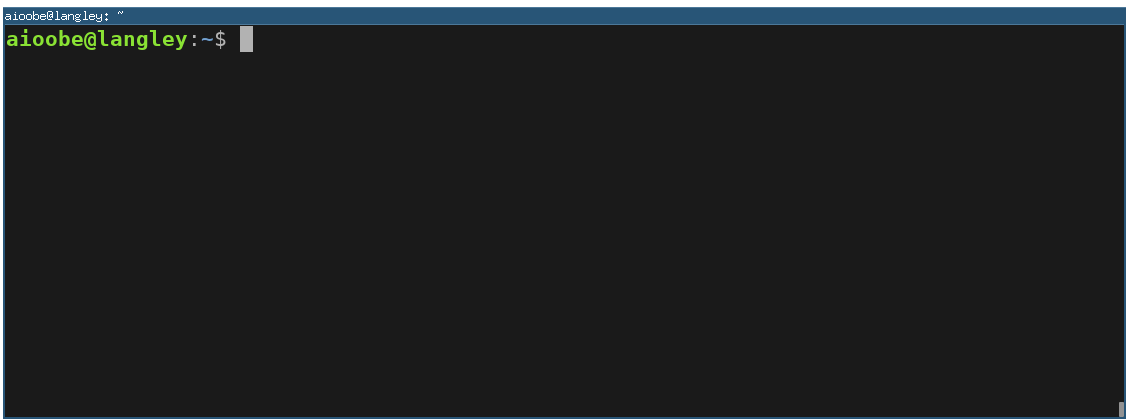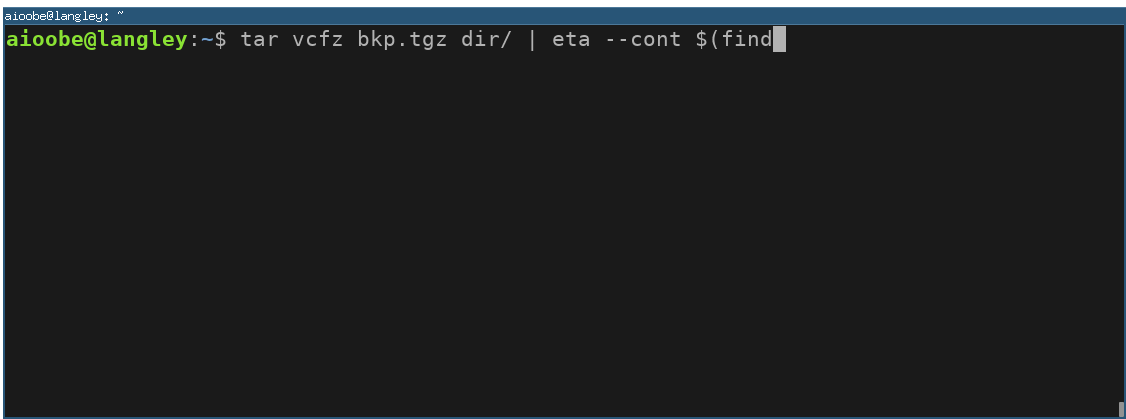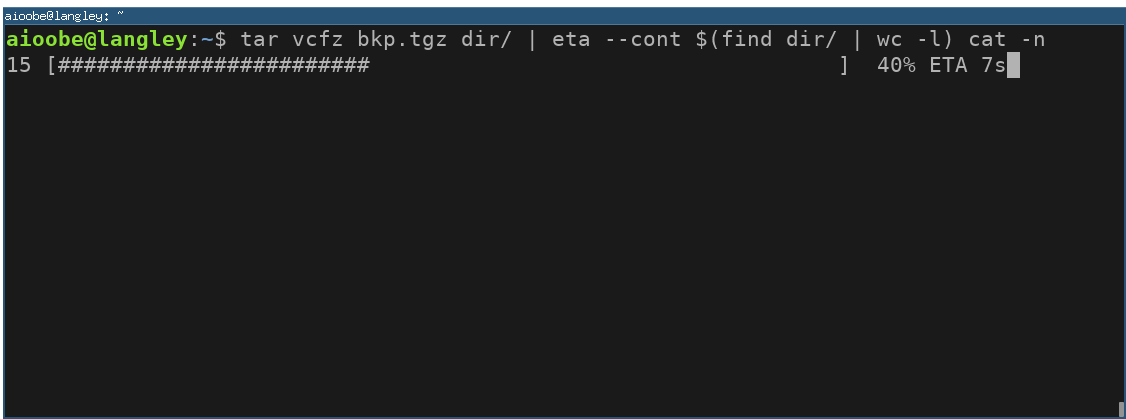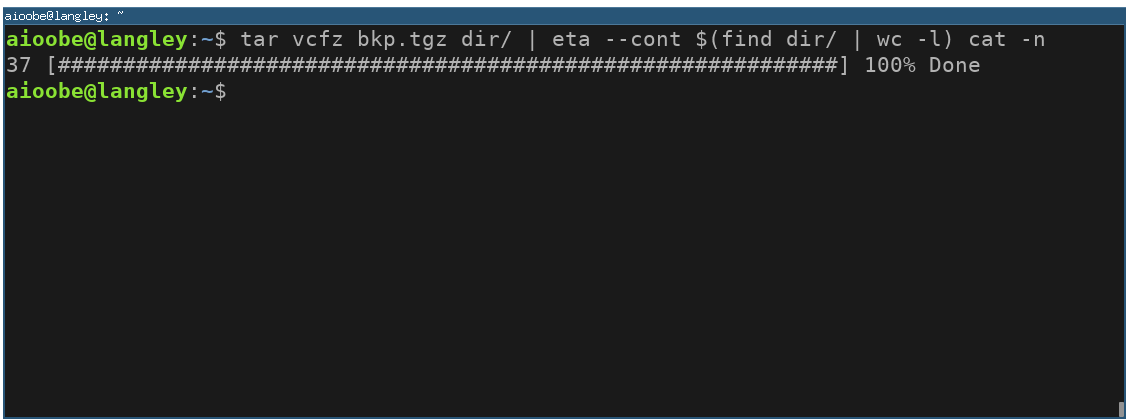
With --cont the progress command is kept running, and the progress is determined by reading the output line by line continuously.
You can use cat -n to add line numbers to the output of a command. The line numbers can then be used as a progress indicator. For example, since tar v... prints one file per line, the progress can be monitored by counting lines as follows:
Use --down if the progress value decreases.