-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 111
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
7 changed files
with
345 additions
and
195 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,240 @@ | ||
| (devguide-setup)= | ||
|
|
||
| # Developer Guide | ||
|
|
||
| The hvPlot library is a project that provides a wide range of data interfaces and an extensible set of plotting backends, which means the development and testing process involves a broad set of libraries. | ||
|
|
||
| This guide describes how to install and configure development environments. | ||
|
|
||
| If you have any problems with the steps here, please reach out in the `dev` channel on [Discord](https://discord.gg/rb6gPXbdAr) or on [Discourse](https://discourse.holoviz.org/). | ||
|
|
||
| ## TL;DR | ||
|
|
||
| 0. Open an [issue on Github](https://github.com/holoviz/hvplot/issues) if needed | ||
| 1. Fork and clone [hvPlot's Github repository](https://github.com/holoviz/hvplot) | ||
| 2. Install [`pixi`](https://pixi.sh) | ||
| 3. Run `pixi run install-dev` to create your development environment | ||
| 4. Make some changes and run: | ||
| - `pixi run test-unit` if you updated the source code to run the unit tests | ||
| - `pixi run test-example` if you updated the notebooks to run them | ||
| - `pixi run docs-build-dev` if you need to build the website locally | ||
| 5. Open a Pull Request | ||
|
|
||
| ## Preliminaries | ||
|
|
||
| ### Basic understanding of how to contribute to Open Source | ||
|
|
||
| If this is your first open-source contribution, please study one | ||
| or more of the below resources. | ||
|
|
||
| - [How to Get Started with Contributing to Open Source | Video](https://youtu.be/RGd5cOXpCQw) | ||
| - [Contributing to Open-Source Projects as a New Python Developer | Video](https://youtu.be/jTTf4oLkvaM) | ||
| - [How to Contribute to an Open Source Python Project | Blog post](https://www.educative.io/blog/contribue-open-source-python-project) | ||
|
|
||
| ### Git | ||
|
|
||
| The hvPlot source code is stored in a [Git](https://git-scm.com) source control repository. The first step to working on hvPlot is to install Git onto your system. There are different ways to do this, depending on whether you use Windows, Mac, or Linux. | ||
|
|
||
| To install Git on any platform, refer to the [Installing Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-Installing-Git) section of the [Pro Git Book](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2). | ||
|
|
||
| To contribute to hvPlot, you will also need [Github account](https://github.com/join) and knowledge of the [_fork and pull request workflow_](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/quickstart/contributing-to-projects). | ||
|
|
||
| ### Pixi | ||
|
|
||
| Developing all aspects of hvPlot requires a wide range of packages in different environments, but for new contributors the `default` environment will be more than enough. | ||
|
|
||
| To make this more manageable, Pixi manages the developer experience. To install Pixi, follow [this guide](https://pixi.sh/latest/#installation). | ||
|
|
||
| #### Glossary | ||
|
|
||
| - *Tasks*: A task is what can be run with `pixi run <task-name>`. Tasks can be anything from installing packages to running tests. | ||
| - *Environments*: An environment is a set of packages installed in a virtual environment. Each environment has a name; you can run tasks in a specific environment with the `-e` flag. For example, `pixi run -e test-core test-unit` will run the `test-unit` task in the `test-core` environment. | ||
| - *Lock-file*: A lock-file is a file that contains all the information about the environments. | ||
|
|
||
| For more information, see the [Pixi documentation](https://pixi.sh/latest/). | ||
|
|
||
| :::{admonition} Note | ||
| :class: info | ||
|
|
||
| The first time you run `pixi`, it will create a `.pixi` directory in the source directory. | ||
| This directory will contain all the files needed for the virtual environments. | ||
| The `.pixi` directory can be large, so it is advised not to put the source directory into a cloud-synced directory. | ||
|
|
||
| ::: | ||
|
|
||
| ## Installing the Project | ||
|
|
||
| ### Cloning the Project | ||
|
|
||
| The source code for the hvPlot project is hosted on [GitHub](https://github.com/holoviz/hvplot). The first thing you need to do is clone the repository. | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Go to [github.com/holoviz/hvplot](https://github.com/holoviz/hvplot) | ||
| 2. [Fork the repository](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/quickstart/contributing-to-projects#forking-a-repository) | ||
| 3. Run in your terminal: `git clone https://github.com/<Your Username Here>/hvplot` | ||
|
|
||
| The instructions for cloning above created a `hvplot` directory at your file system location. | ||
| This `hvplot` directory is the _source checkout_ for the remainder of this document, and your current working directory is this directory. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Start developing | ||
|
|
||
| To start developing, run the following command, this will create an environment called `default` (in `.pixi/envs`), install hvPlot in [editable mode](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/topics/local-project-installs/#editable-installs), download test datasets, and install `pre-commit`: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| pixi run install-dev | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| :::{admonition} Note | ||
| :class: info | ||
|
|
||
| The first time you run it, it will create a `pixi.lock` file with information for all available environments. | ||
| This command will take a minute or so to run. | ||
| ::: | ||
|
|
||
| All available tasks can be found by running `pixi task list`, the following sections will give a brief introduction to the most common tasks. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Syncing Git tags with upstream repository | ||
|
|
||
| If you are working from a forked repository of hvPlot, you will need to sync the tags with the upstream repository. | ||
| This is needed because the hvPlot version number depends on [`git tags`](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Basics-Tagging). | ||
| Syncing the git tags can be done with: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| pixi run sync-git-tags | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Developer Environment | ||
|
|
||
| The `default` environment is meant to provide all the tools needed to develop hvPlot. | ||
|
|
||
| This environment is created by running `pixi run install-dev`. Run `pixi shell` to activate it; this is equivalent to `source venv/bin/activate` in a Python virtual environment or `conda activate` in a conda environment. | ||
|
|
||
| If you need to run a command directly instead of via `pixi`, activate the environment and run the command (e.g. `pixi shell` and `pytest hvplot/tests/<somefile.py>`). | ||
|
|
||
| ### VS Code | ||
|
|
||
| This environment can also be selected in your IDE. In VS Code, this can be done by running the command `Python: Select Interpreter` and choosing `{'default': Pixi}`. | ||
|
|
||
| <p style="text-align: center"> | ||
| <img | ||
| src="https://assets.holoviews.org/static/dev_guide/001.png" | ||
| alt="001" | ||
| style="width: 45%; display: inline-block" | ||
| /> | ||
| <img | ||
| src="https://assets.holoviews.org/static/dev_guide/002.png" | ||
| alt="002" | ||
| style="width: 45%; display: inline-block" | ||
| /> | ||
| </p> | ||
|
|
||
| To confirm you are using this dev environment, check the bottom right corner: | ||
|
|
||
| 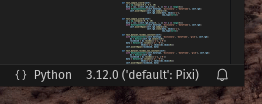 | ||
|
|
||
| ### Jupyter Lab | ||
|
|
||
| You can launch Jupyter lab with the `default` environment with `pixi run lab`. This can be advantageous when you need to edit the documentation or debug an example notebook. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Linting | ||
|
|
||
| hvPlot uses [`pre-commit`](https://pre-commit.com/) to lint and format the source code. `pre-commit` is installed automatically when running `pixi run install-dev`; it can also be installed with `pixi run lint-install`. | ||
| `pre-commit` runs all the linters when a commit is made locally. Linting can be forced to run for all the files with: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| pixi run lint | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| :::{admonition} Note | ||
| :class: info | ||
|
|
||
| Alternatively, if you have `pre-commit` installed elsewhere you can run: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| pre-commit install # To install | ||
| pre-commit run --all-files # To run on all files | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ::: | ||
|
|
||
| ## Testing | ||
|
|
||
| To help keep hvPlot maintainable, all Pull Requests (PR) with code changes should typically be accompanied by relevant tests. While exceptions may be made for specific circumstances, the default assumption should be that a Pull Request without tests will not be merged. | ||
|
|
||
| There are three types of tasks and five environments related to tests. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Unit tests | ||
|
|
||
| Unit tests are usually small tests executed with [pytest](https://docs.pytest.org). They can be found in `hvplot/tests/`. | ||
| Unit tests can be run with the `test-unit` task: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| pixi run test-unit | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| :::{admonition} Advanced usage | ||
| :class: tip | ||
|
|
||
| The task is available in the following environments: `test-39`, `test-310`, `test-311`, `test-312`, and `test-core`. Where the first ones have the same environments except for different Python versions, and `test-core` only has a core set of dependencies. | ||
|
|
||
| You can run the task in a specific environment with the `-e` flag. For example, to run the `test-unit` task in the `test-39` environment, you can run: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| pixi run -e test-39 test-unit | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ::: | ||
|
|
||
| :::{admonition} Advanced usage | ||
| :class: tip | ||
|
|
||
| Currently, an editable install needs to be run in each environment. So, if you want to install in the `test-core` environment, you can add `--environment` / `-e` to the command: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| pixi run -e test-core install | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ::: | ||
|
|
||
| ### Example tests | ||
|
|
||
| hvPlot's documentation consists mainly of Jupyter Notebooks. The example tests execute all the notebooks and fail if an error is raised. Example tests are possible thanks to [nbval](https://nbval.readthedocs.io/) and can be found in the `doc/` folder. | ||
| Example tests can be run with the following command: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| pixi run test-example | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Documentation | ||
|
|
||
| The documentation can be built with the command: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| pixi run docs-build-dev | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| As hvPlot uses notebooks for much of the documentation, this takes a little while. You can disable building the gallery by setting the environment variable `HVPLOT_REFERENCE_GALLERY` to `false`. | ||
|
|
||
| A development version of hvPlot can be found [here](https://holoviz-dev.github.io/hvplot/). You can ask a maintainer if they want to make a dev release for your PR, but there is no guarantee they will say yes. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Build | ||
|
|
||
| hvPlot has two build tasks to build a Python (for pypi.org) and a Conda package (for anaconda.org). | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| pixi run build-pip | ||
| pixi run build-conda | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Continuous Integration | ||
|
|
||
| Every push to the `main` branch or any PR branch on GitHub automatically triggers a test build with [GitHub Actions](https://github.com/features/actions). | ||
|
|
||
| You can see the list of all current and previous builds at [this URL](https://github.com/holoviz/hvplot/actions) | ||
|
|
||
| ### Etiquette | ||
|
|
||
| GitHub Actions provides free build workers for open-source projects. A few considerations will help you be considerate of others needing these limited resources: | ||
|
|
||
| - Run the tests locally before opening or pushing to an opened PR. | ||
|
|
||
| - Group commits to meaningful chunks of work before pushing to GitHub (i.e., don't push on every commit). |
Oops, something went wrong.