This is a Python implementation of ButtonFever, from mickey9801, intended to be used on Micropython port for ESP32. The following is an adaptation of its documentation.
Powerful button tools for managing various button events of standalone button or button array. Tested on ESP32 with MicroPython.
Button class handled standalone button debouncing, trigger callback function for single press, double press, and long press events. The class can distinguish different pressing pattern and trigger corresponding callback, i.e. single press vs double press.
ButtonManager class manage multiple buttons with single analog pin. The class also provide print_reading() method for you to check the analog pin reading. In theory you may add more buttons in the circuit.
- Just copy the file
pybuttons.pyfrom this repository inside your proyect and import it.
Button class can be used alone to handle press event of a single digital button.
-
Import
Buttonclassfrom pybuttons import Button
-
Create button object
btn = Button(mode, pin, pullup, button_logic)
By default, the object will use internal pullup of the board, but you may also use external pullup/pulldown as example you concern, e.g. awake from deep sleep mode using button.
Parameters:
Parameter Description mode Declare button mode. Assign Button.MODE_DIGITALfor standalone digital button.pin GPIO of the button pullup=True Use internal pullup button_logic=Button.LOW Button logic. Possible value: Button.HIGH(pulldown) orButton.LOW(pullup, default)btn_pin = 12 btn = Button(Button.MODE_DIGITAL, btn_pin, False, Button.HIGH) # using external pulldown
-
Declare button callback
Button callback must contain 2 parameters:
Parameter Description btn Button object itself pattern Press pattern of the event. Possible value: - Button.SINGLE_PRESS
- Button.DOUBLE_PRESS
- Button.LONG_PRESS
You may declare different callback for different press pattern, or you may use single callback for all patterns.
def press_handler(btn, pattern): print("button id {} ".format(btn.get_id()), end="") if pattern == Button.SINGLE_PRESS: print("pressed.") elif pattern == Button.DOUBLE_PRESS: print("double pressed.") elif pattern == Button.LONG_PRESS: print("long pressed.")
-
Assign callback for button press events
btn.on_press(press_handler) .on_double_press(press_handler) # default timeout .on_press_for(press_handler, 1000) # custom timeout for 1 second
-
on_press(callback)Single press event handler
-
on_double_press(callback, timeout=300)Detect double press within timeout.
-
on_press_for(callback, timeout=3000)Trigger long press event when continue pressed for a while (ie.
timeout).
-
-
In your event loop, read button status.
while True: # ... do other things here btn.read()
NOTE: if you use the same pin for digital after being used as analog, you may need to do a hard-reset of the device to change its internal configuration (sometimes even a whole power-off/power-on cycle).
from pybuttons import Button
# change according to your needs
PIN = 36
def press_handler(btn, pattern):
print("button id {} ".format(btn.get_id()), end="")
if pattern == Button.SINGLE_PRESS:
print("pressed.")
elif pattern == Button.DOUBLE_PRESS:
print("double pressed.")
elif pattern == Button.LONG_PRESS:
print("long pressed.")
btn = Button(Button.MODE_DIGITAL, PIN, False, Button.HIGH)
btn.on_press(press_handler) \
.on_double_press(press_handler) \
.on_press_for(press_handler, 1000)
while True:
btn.read()ButtonManager class manage multiple buttons with single analog pin.
To determine voltage range for each button in the array, you may check the actual readings with print_reading() method.
The following script calculate the avarage reading of a button from 5 readings:
import time
from pybuttons import ButtonManager
# change according to your needs
PIN = 36
sum_ = i = 0
while True:
reading = ButtonManager.print_reading(PIN)
# button pressed
if reading > 100:
sum_ += reading
i += 1
if i > 4:
print("Average Reading: {}".format(sum_ / i))
sum_ = i = 0
# button released
else:
sum_ = i = 0
time.sleep_ms(200)NOTE: Readings of analog pin may vary upon other connected devices. Voltage ranges for each button should determine based on measurement of the final circuit with all required devices initialized.
-
Import
Buttonclass andButtonManagerclassfrom pybuttons import Button, ButtonManager
-
Create
ButtonMmanagerobjectmanager = ButtonManager(pin, btn_num)
Parameters:
Parameter Description pin Analog pin of the button array btn_num Number of buttons in the array btn_pin = 35 manager = ButtonManager(btn_pin, 4)
-
Create
Buttonobjects and assign an ID for the buttonButton(mode, id)
Parameters:
Parameter Description mode Declare button mode. Assign Button.MODE_ANALOG_ARRAYfor button in button array.id ID of the button btn0 = Button(Button.MODE_ANALOG_ARRAY, 0) btn1 = Button(Button.MODE_ANALOG_ARRAY, 1) btn2 = Button(Button.MODE_ANALOG_ARRAY, 2) btn3 = Button(Button.MODE_ANALOG_ARRAY, 3)
-
Declare button callback
(see above: Standalone Button Usage)
-
Assign callback to events
(see above: Standalone Button Usage)
-
Add button to button manager and provide the voltage range of the button
add_button(btn, min_volt_reading, max_volt_reading)
Parameters:
Parameter Description btn Button object min_volt_reading Minimum voltage reading of the button max_volt_reading Maximum voltage reading of the button manager.add_button(btn0, 3100, 3500)
-
Initialize button manager for reading analog pin
manager.begin()
-
In your event loop, update button state
while True: # ... do other things here manager.loop()
from pybuttons import Button, ButtonManager
# change according to your needs
PIN = 36
def press_handler(btn, pattern):
print("button id {} ".format(btn.get_id()), end="")
if pattern == Button.SINGLE_PRESS:
print("pressed.")
elif pattern == Button.DOUBLE_PRESS:
print("double pressed.")
elif pattern == Button.LONG_PRESS:
print("long pressed.")
def special_press_handler(btn, pattern):
print("button id {} is special!!".format(btn.get_id()))
manager = ButtonManager(PIN, 4)
manager.set_adc_resolution(4096)
btn0 = Button(Button.MODE_ANALOG_ARRAY, 0)
btn1 = Button(Button.MODE_ANALOG_ARRAY, 1)
btn2 = Button(Button.MODE_ANALOG_ARRAY, 2)
btn3 = Button(Button.MODE_ANALOG_ARRAY, 3)
btn0.on_press(press_handler)
btn0.on_double_press(press_handler)
btn0.on_press_for(press_handler, 2000)
manager.add_button(btn0, 3100, 3500)
btn1.on_press(press_handler)
btn1.on_press_for(press_handler, 1500)
manager.add_button(btn1, 2200, 2800)
btn2.on_press_for(press_handler, 1000) \
.on_press(press_handler) \
.on_double_press(special_press_handler, 300)
manager.add_button(btn2, 1500, 2000)
btn3.on_press(press_handler)
manager.add_button(btn3, 600, 1000)
manager.begin()
while True:
manager.loop()-
get_id()Return button pin number for digital button, or ID for button in button array.
-
get_pin()Alias of getID().
-
set_adc_resolution(resolution)Set resolution for ADC. The library will set build-in ADC for ESP32 by default.
-
print_reading(pin)Print analog pin reading through Serial port and return the reading.
reading = ButtonManager.print_reading(36)
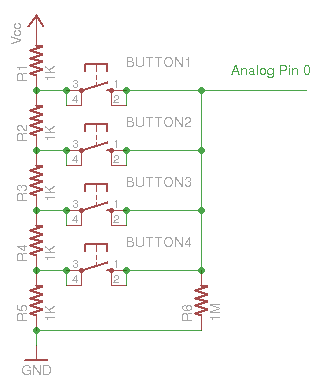
- Vout = Vin(R2/R1+R2)
- Vin = 3.3V # ESP32
- R1+R2 = 5KΩ = 5000Ω
- Button 1 Vout = 3.3(4000/5000) = 2.64V
- Button 2 Vout = 3.3(3000/5000) = 1.98V
- Button 3 Vout = 3.3(2000/5000) = 1.32V
- Button 4 Vout = 3.3(1000/5000) = 0.66V
0 ~ 3.3V = 0 ~ 4095 3.3V/4095 = 0.81mV
| Button | MultiMeter Measurement | Expected Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.62V | 3259 |
| 2 | 1.96V~1.97V | 2420~2432 |
| 3 | 1.30V~1.31V | 1605~1617 |
| 4 | 0.65V | 802 |
It is required an adjustment for ESP32 ADC with the following equation:
Vout = e / 4095.0 * 3.3 + 0.1132
| Button | Circuit Measurement | Serial Debug Data | Calculated Voltage w' Adjustment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.61V | 3070~3103 | 2.59V~2.61V |
| 2 | 1.95V~1.96V | 2237~2255 | 1.92V~1.93V |
| 3 | 1.30V | 1456~1461 | ~1.29V |
| 4 | 0.64V~0.65V | 658~664 | 0.64V~0.65V |